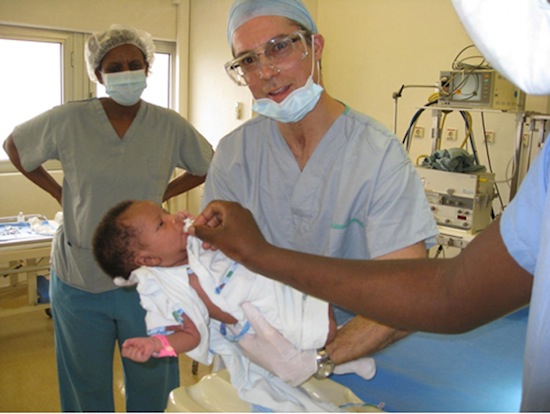
Dr. Neil Pollock, second from the left, in Haiti. (photo from Neil Pollock)
Vancouver-based Dr. Neil Pollock has recently returned from a mission to Haiti, where he trained surgeons in newborn male circumcision to help fight against HIV.
Among other benefits, “circumcision reduces AIDs transmission by 60 percent and that would reduce a man’s risk of acquiring HIV. The reason is, the foreskin has receptor cells that selectively bind the HIV virus and promote its uptake into the body. So, by removing the foreskin, you remove the portal of entry for the virus,” explained Pollock, who specializes in circumcision and adult vasectomy.
Pollock was approached to lead the Haiti mission by Dr. Jeffrey Klausner, a medical doctor and professor of medicine at UCLA, specializing in infectious disease. Klausner volunteers with GHESKIO, a nongovernmental organization run out of the Centre for Global Health at Weill Cornell Medical College in partnership with the Haitian government.
In a phone interview with the Independent, Klausner said that, around 2007/08, “evidence became very clear that circumcision was a highly effective prevention intervention for HIV and the first priority was to get adolescents and young men circumcised. And, over time, we scaled up progress for newborns.”
After moving from South Africa to Los Angeles, Klausner started working in various countries. It was in Haiti in March 2012 that he connected with GHESKIO. He said it was one of the first NGOs to respond to the AIDs crisis in the early 1980s. Through GHESKIO, he was introduced to Haiti’s first lady, Sophia Martelly, in Washington, D.C., at the International AIDs Conference. Klausner said that, when talking to Martelly about the prospect of introducing newborn circumcision to Haiti, she said, “Absolutely, we’d love to do that, but we don’t have the resources, we don’t have the technical expertise, so we really need to rely on people like you to help us.”
Klausner returned to GHESKIO and worked to organize “a physical place, the proper clean procedure room … certain types of equipment and supplies and autoclaves, sterilized surgical equipment, and the tab was running into tens of thousands, about $50,000…. Once we had the supplies and materials, then the next step was to get the training, and I’m not a surgeon. I contacted the head of circumcision programs in Kenya, a guy named Robert Bailey.”
Bailey directed Klausner to Pollock. Klausner said he was “encouraged by [Pollock’s] enthusiasm and … set up a training program for May 2014.” (see jewishindependent.ca/vancouver-doctor-will-train-doctors-in-haiti-in-circumcision) However, the mission had to be postponed to November, as just days before they were set to depart, an “outbreak of chikungunya fever hit, which is a rare [virus] that causes fever, joint pain, and about one of 100 people can get lifelong arthritis.” In addition, “there was a fire in a supply room and we lost some of the tables we had bought and one of the autoclaves,” and “a box of supplies went missing.”
Despite these and other challenges in organizing and executing the mission, such as difficulties in communication due to power outages and poor internet connections, Klausner said, “I have been doing international work, research and programs for 25 years now and [obstacles are] par for the course. This actually went smoother than many other projects [in which] I have been involved.”
For the Haiti mission, said Klausner, “We had to make sure there were at least 200 parents and babies that were already pre-examined, pre-consented, pre-educated and prepared” because for “a training program like this to be successful you really need to do between 50 to 100 [surgeries] a day in a short period with a lot of cases to make sure the people you are training learn, and learn effectively so they can go on and do this independently and confidently.”
Pollock said he had “arranged to train two surgeons, in case one of them did not have the aptitude to succeed – in the end, one did not, and it was difficult of course to tell him that, but it was clear that it would not be safe to pass him and enable him to operate on patients.”
With the use of the technique he taught in Haiti, said Pollock, recovery time will be reduced compared to current Haitian practices “because there is so little trauma caused during surgery.”
Klausner offered three measures for the mission’s success. “One is the actual conduct of safe, well-done circumcision on the babies that Dr. Pollock and his colleague Pierre Crouse did. That’s an achievement in itself: they did over 100 infants in two and a half days. The second part is that the surgeon and the teams that were trained, they continue to do it themselves, so they have done an additional 100 since we left. And then the third piece is that we have trained the trainers, and now other teams are being trained” to perform the surgery.
Klausner’s and Pollock’s efforts in combating HIV and AIDs received notice from some high-profile celebrities. “I was quite surprised to get a text from Sean Penn on the day after we landed in Port-au-Prince that he wanted to come down and meet and observe what myself and my team were doing and discuss synergies between our global interests in promoting health care,” said Pollock. Penn was joined by Charlize Theron, “who was also interested in discussing collaborative efforts in association with her foundation helping improve health care for the people in her native country of South Africa.”
Klausner said, “I have been working in eastern South Africa, KwaZulu-Natal province … with the public health leaders there to introduce a similar effort where we would train surgeons, create a permanent resource, such as a training program, to expand the number of trained doctors or medical officers in newborn circumcision.” In that province, he said, “40 percent of people have HIV infection” and “75 percent of women aged 30 have HIV. So, right now, that part of South Africa … is in a complete, out of control, HIV epidemic. I helped introduce adult circumcision there, but I think, to have greater impact in the long term, we need to introduce newborn circumcision.”
He added, “I believe Dr. Pollock had a very positive experience [in Haiti] and I suspect he is optimistic about the possibility to go and do it again elsewhere.”
Zach Sagorin is a Vancouver freelance writer.