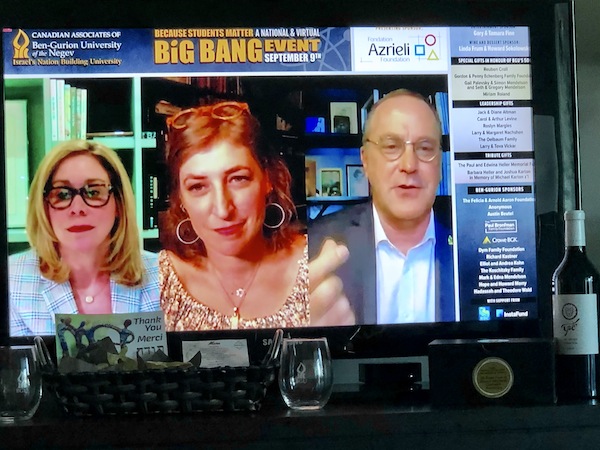
Left to right, Senator Linda Frum, actor Mayim Bialik and BGU president Danny Chamovitz participated in the virtual Big Bang event, hosted by Canadian Associates of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev on Sept. 9. (photo by David Berson)
On Sept. 9, the Canadian Associates of Ben-Gurion University of the Negev hosted its first national virtual gathering. The Big Bang Event to “save the class of COVID-19” was an urgent move to support the university’s 20,000 students.
With many students having lost their jobs in the sudden economic slowdown, they are unable to fund their tuition or even their basic needs. Rather than forfeiting a generation of leaders to financial hardship, BGU launched a student assistance program in July, with the goal of raising $6 million for 6,000 individuals.
While it is Israel’s newest university, BGU is a leader in academic research and technological development. With three campuses, it is credited as a trailblazer in both the humanities and the sciences – nanotechnology, robotics, cybersecurity, Israel studies, Jewish thought, neuroscience, medicine, business and management – addressing some of the world’s biggest problems, such as drought and hunger. The university’s reach is local as well as international, serving the immediate community in the Negev, including both the immigrant and indigenous Bedouin populations.
BGU was founded in 1969, following the vision of David Ben-Gurion, Israel’s first prime minister. Ben-Gurion sought to establish a university which would act as a “source of moral inspiration and courage, rousing people to a sense of mission: noble, creative and fruitful.” He believed that the Negev Desert would be critical to the future of the new country – the desert covers 60% of the country, and Ben-Gurion saw it becoming an economic, academic, scientific and cultural hub.
The Big Bang Event featured guest speaker Mayim Bialik, well-known for her roles in the 1990s show Blossom and, more recently, in her award-winning role as Amy Farrah Fowler in Big Bang Theory. In addition to acting, Bialik earned a doctorate in neuroscience from the University of California, Los Angeles, in 2007; her dissertation examined the role of oxytocin and vasopressin in obsessive-compulsive disorder in adolescents with Prader-Willi syndrome. A mother of two, Bialik is also an accomplished writer and musician.
Quirky, vivacious and searingly intelligent in her remarks, watching her speak at the Big Bang Event brought to mind the Yiddish proverb, “The heart is small and it embraces the whole wide world.” Bialik spoke from the heart, telling the audience about her own family story and the genesis of her Jewish identity. She spoke about her heritage, how she raised her children and how she carries her Jewish identity into her professional life in a fireside chat-style with Canadian Senator Linda Frum.
Also speaking at the event was BGU president Danny Chamovitz, who addressed the audience from his home in Israel at what would have been 2:30 a.m. his time. Chamovitz was in isolation, having recently returned from Europe, and, following the event, he did indeed test positive for coronavirus, but has since made a full recovery.
Chamovitz described his office’s emergency response to the pandemic. Members of the university community were invited to submit proposals and, as a result, more than 70 initiatives are in progress, including the development of tests for COVID-19 that drastically reduce turnaround times.
“Across the country, more than 380 households purchased tickets and more than 800 people watched the program,” said David Berson, CABGU regional executive director, in a recent email interview. “We have raised over $1.3 million with 50% of that being raised locally. In our region, 83 households purchased tickets and more than 200 people watched the program.”
In addition to raising money, he said, “The event was a great success motivating many new people to support CABGU. It has set the bar, the gold standard, for how to properly execute a national virtual event. Regarding the campaign itself, the rate of unemployment in Israel is 50% for the under-34 age bracket. By the opening of the academic year on Oct. 18, more than 5,000 students had applied for support from this student assistance fund. Where we had been fearful that enrolment would drop because of the financial impact of the pandemic, it turns out that enrolment for undergrad studies increased by 32%. The funds raised have been vital in creating accessibility for so many students hit hard by this unprecedented situation.”
While the Big Bang audience was scattered from coast to coast, a warm ambience was created locally, with hand-delivered baskets of sweet and savoury delicacies: quiches and bourekas, as well as exquisitely decorated handmade chocolates, from Café FortyOne; and BGU wine tumblers and a bottle of red wine.
The local business sponsor was Instafund and Instafund’s Adam Korbin, who was the Metro Vancouver chair of the event, thanked Bialik at the end of the program.
“We were very fortunate to have dozens of local sponsors for the event,” said Berson. “Details of the sponsors can be found on our website, bengurion.ca.”
Regional board chair Si Brown “was thrilled with the generous response from and participation of our local community,” Berson added. “Since reestablishing CABGU in Metro Vancouver seven years ago, it has been gratifying for me to watch how our community has slowly and surely begun to embrace this young and dynamic Israeli university in the Negev.”